THE MERIDIAN SYSTEM AND ACUPUNCTURE
According the traditional Chinese medicine theory, our body consists of a giant web called the meridian system linking different parts and organs of the body. Its channels makes up a comprehensive yet complex body map that supplies Qi and assists with distribution of blood and body fluids all over the body, maintain the balance between the Yin and Yang and protects body against the diseases. Along these channels, acupuncture points are the sites through which Qi of the organs and meridians is transported to the body surface. When the body gets ill, acupuncturist work on these points to regulate corresponding organs or meridians so that the body can return to state of balance and health.
The Huang Di Nei Jing in The Yellow Emperor's Classic of Internal Medicine says: "The twelve Meridian system is the process through which our body grows, the explanation how disease continues and develops, the method by which our body is treated, the concept where philosophy begins, the target where successful target should be achieved". This saying illustrates the importance of meridian theory in human physiology, pathology and diagnosis in TCM.
Physiological application
"The Meridians move Qi and Blood. As a result Yin and Yang get regulated. Tendons and bones get nourished. Joints get facilitated" (Huang Di Nei Jing. The Yellow Emperor's Classic of Internal Medicine).
Meridians work like a network system transporting and distributing Qi and Blood, linking up organs, bones, joints, tendons, skin and providing communication between body's exterior and interior. Through healthy Meridian system Qi and Blood warm and nourish different organs and tissues and maintain normal metabolic activities. Also Meridians are essential in supporting the flow of nutritive Qi (Ying) inside the blood vessels and the flow of protective Qi (Wei) around them. In addition they strength the body's immune system, protects against external pathogens and assist in regulating Yin and Yang.
Pathological application
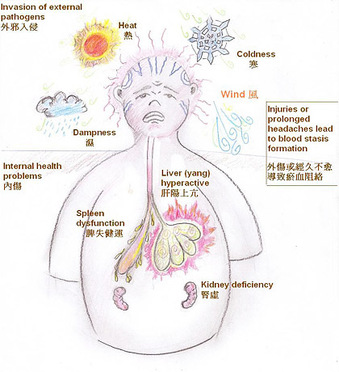
External pathogens "evils" transform and progress along the meridians to attack the body and cause disease. In Chinese Medicine they are classified as Wind, Fire, Dampness, Dryness, Cold and Summer Heat. The "evils" can proceed from exterior to interior or travel from one organ to another.
For example, common influenza is due to attack of Wind and Cold, which attack the most superficial meridians Lung and Bladder with the symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, headache, aversion to cold and general weakness. If not treated, cold can easily turn to heat, the pathogens can penetrate to interior and attack organs causing high fever, sore throat, pneumonia etc.
The Huang Di Nei Jing in The Yellow Emperor's Classic of Internal Medicine says: "The twelve Meridian system is the process through which our body grows, the explanation how disease continues and develops, the method by which our body is treated, the concept where philosophy begins, the target where successful target should be achieved". This saying illustrates the importance of meridian theory in human physiology, pathology and diagnosis in TCM.
Physiological application
"The Meridians move Qi and Blood. As a result Yin and Yang get regulated. Tendons and bones get nourished. Joints get facilitated" (Huang Di Nei Jing. The Yellow Emperor's Classic of Internal Medicine).
Meridians work like a network system transporting and distributing Qi and Blood, linking up organs, bones, joints, tendons, skin and providing communication between body's exterior and interior. Through healthy Meridian system Qi and Blood warm and nourish different organs and tissues and maintain normal metabolic activities. Also Meridians are essential in supporting the flow of nutritive Qi (Ying) inside the blood vessels and the flow of protective Qi (Wei) around them. In addition they strength the body's immune system, protects against external pathogens and assist in regulating Yin and Yang.
Pathological application
External pathogens "evils" transform and progress along the meridians to attack the body and cause disease. In Chinese Medicine they are classified as Wind, Fire, Dampness, Dryness, Cold and Summer Heat. The "evils" can proceed from exterior to interior or travel from one organ to another.
For example, common influenza is due to attack of Wind and Cold, which attack the most superficial meridians Lung and Bladder with the symptoms such as sneezing, coughing, headache, aversion to cold and general weakness. If not treated, cold can easily turn to heat, the pathogens can penetrate to interior and attack organs causing high fever, sore throat, pneumonia etc.
In one organ disharmony other organs can be affected: disharmony of Liver, like Liver Qi stagnation or Liver Heat can effect Stomach/Spleen Qi - digestion. Moreover, organ disharmony can manifest along its whole meridian: ulcers on the tip of the tongue shows suggest Heart disharmony since Heart meridian has its branches at the tip of tongue. Moreover, in Chinese medicine Heart opens into the tongue.
References:
Kaptchuk T., 2000. Chinese Medicine:The web that has no Weather. London: Rider
Application of Meridian Theory. http://www.shen-nong.com/eng/principles/applicationmeridian.html#phy
References:
Kaptchuk T., 2000. Chinese Medicine:The web that has no Weather. London: Rider
Application of Meridian Theory. http://www.shen-nong.com/eng/principles/applicationmeridian.html#phy